What is Diecast Printing
Diecast printing is a specialized form of printing used to decorate or add markings to diecast models. These models, typically made of metal alloys, are popular among collectors and hobbyists. This process allows for the addition of detailed graphics, logos, and designs, enhancing the aesthetic appeal and realism of the models. The techniques employed in diecast printing are designed to adhere effectively to the metallic surfaces, ensuring durability and longevity of the printed images. Understanding the basics of diecast printing is essential for anyone looking to customize or produce high-quality diecast models. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced modeler, knowing the ins and outs of this process can significantly improve your results and bring your creative visions to life.
The Diecast Printing Process Explained
The diecast printing process involves several key steps, each crucial for achieving a successful print. First, the diecast model undergoes surface preparation to ensure optimal ink adhesion. This often includes cleaning and priming the surface. Next, the desired design or artwork is transferred onto the model using one of several printing techniques. After the design is applied, the ink needs to cure or dry, a process that depends on the type of ink and printing method used. This curing stage is vital for the durability and longevity of the print. Finally, the model may undergo finishing touches, such as clear coating, to protect the print and further enhance its appearance. Each of these steps must be carefully executed to ensure the final product meets the desired quality standards.
Types of Diecast Printing Techniques

Several printing techniques are commonly used for diecast models. Each technique has its own advantages and is suited for different types of designs and production scales. The choice of technique often depends on factors such as the complexity of the design, the required level of detail, and the volume of models to be printed. Understanding the differences between these techniques is crucial for choosing the best method for your specific needs. Moreover, each method requires specific equipment, inks, and expertise, influencing the overall printing process and the final outcome of the diecast model’s decoration.
Pad Printing
Pad printing is a versatile technique widely used for diecast models. It involves transferring a two-dimensional image onto a three-dimensional object using a silicone pad. This method is particularly effective for applying detailed graphics and designs onto curved or uneven surfaces. Pad printing offers excellent precision and is suitable for mass production. The process typically begins with a printing plate containing the desired image, which is etched with the design. Ink is applied to the plate and then picked up by the silicone pad. The pad then transfers the ink onto the diecast model. Pad printing is known for its ability to produce high-quality, durable prints, making it a popular choice among diecast model manufacturers.
Tampo Printing
Tampo printing is another term for pad printing, though the term ’tampo’ is more commonly used to describe the printing process. It is a method that uses a silicone pad to transfer images from a plate to the diecast model. This technique is ideal for printing on irregular surfaces or in tight spaces, and can handle intricate designs with accuracy. The process is often used to apply markings, logos, and other detailed elements onto diecast models. The quality and durability of the print depend on factors such as the type of ink, the pad material, and the preparation of the diecast surface.
Screen Printing
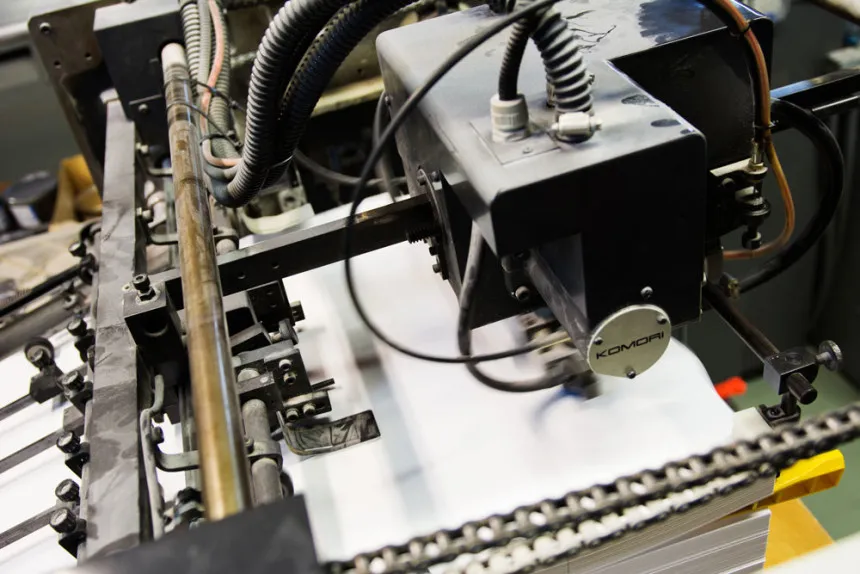
Screen printing involves using a mesh screen to transfer ink onto the diecast model. A stencil is created on the screen, blocking areas where the ink is not desired. Ink is then forced through the open areas of the stencil onto the model’s surface. Screen printing is often used for larger designs or when applying a thicker layer of ink. While it is effective for certain types of graphics, it may not be suitable for highly detailed designs or complex color combinations, especially on curved surfaces. Screen printing is generally less precise than pad printing, making it a better option for simpler designs.
Digital Printing
Digital printing is a more modern approach that allows for direct printing onto the diecast model from a digital file. This method offers great flexibility and is ideal for complex designs, variable data printing, and short production runs. Digital printing can accurately reproduce intricate details and a wide range of colors. It eliminates the need for traditional printing plates, reducing setup time and costs. This technique often employs UV-curable inks, which bond to the surface of the model and quickly cure under ultraviolet light. The precision and versatility of digital printing make it increasingly popular for customized diecast models and prototypes.
Best Materials for Diecast Printing
The selection of materials is crucial for achieving high-quality diecast prints. The ink must adhere well to the diecast metal and be durable enough to withstand handling and environmental factors. The choice of ink often depends on the printing technique and the desired finish. The type of solvents and thinners used during the printing process should also be considered to ensure the inks viscosity is appropriate. In addition to the inks, the surface preparation materials, like primers and cleaners, must be compatible with both the metal and the printing ink. Properly chosen materials will ensure a long-lasting and visually appealing print.
Choosing the Right Printer and Equipment
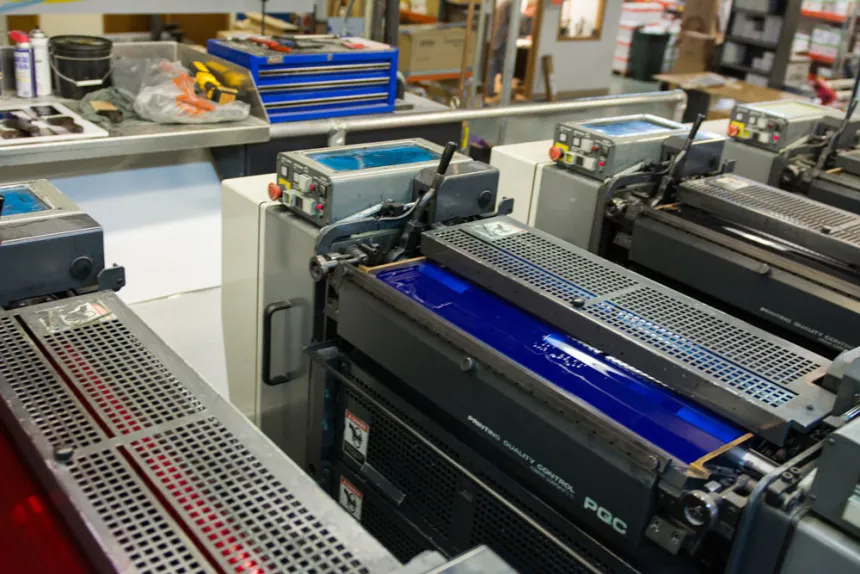

Selecting the right printer and equipment is vital for successful diecast printing. This includes the printing machine itself, which should be compatible with the chosen printing technique (pad, screen, or digital). The printer should be capable of handling the size and shape of your diecast models. Other important equipment includes ink mixers, curing systems (if needed), and any surface preparation tools, such as cleaning stations and priming equipment. It’s important to research and choose equipment that suits your specific needs, budget, and production volume.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Printer
When selecting a printer, several factors should be taken into account. Consider the type of printing technology the printer uses (pad, screen, digital), and ensure it aligns with your design requirements. The print area is another important factor, as it should be large enough to accommodate your largest models. Printing speed, resolution, and the ability to print multiple colors are also important considerations. The printer’s ease of use, maintenance requirements, and support from the manufacturer are also crucial factors to consider. You also need to assess the initial cost, as well as the ongoing operating expenses like ink, consumables, and potential repair costs. Careful evaluation of these factors will ensure that you choose the best equipment to meet your needs.
Ink Selection and Preparation
Ink selection is critical for high-quality diecast printing. The ink must be compatible with the printing process and the metal surface. Different ink formulations are available, including those designed for pad printing, screen printing, and digital printing. Properties like adhesion, flexibility, and durability should be considered. The ink’s color accuracy and opacity are also important, especially for detailed designs. Before printing, the ink may need to be mixed or thinned to achieve the correct viscosity. Proper ink preparation involves ensuring the ink is free from contaminants and is ready for use. Using the right inks and preparing them correctly is essential for ensuring a professional, durable print.
How to Prepare Your Diecast Models for Printing

Surface preparation is a critical step in diecast printing. It involves cleaning and priming the model’s surface to ensure the ink adheres properly and lasts longer. Without proper preparation, the ink may not bond effectively with the metal, resulting in prints that can easily scratch or peel off. Proper surface preparation improves print quality, adhesion, and durability. The goal is to create a surface that is clean, smooth, and ready to receive the ink. This is often the most time-consuming part of the printing process, but it is also one of the most important for guaranteeing a successful print.
Surface Preparation Techniques
Surface preparation techniques include several methods designed to ready the diecast model for printing. These techniques focus on eliminating contaminants and creating an ideal surface for ink adhesion. Effective surface preparation is vital to avoid print defects. This step typically involves cleaning the model to remove dirt, grease, and other residues, followed by priming the surface. Each step plays a critical role in ensuring a high-quality, durable finish.
Cleaning the Diecast Model
Cleaning is the first and often most critical step in surface preparation. The diecast model must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, dust, oil, or other contaminants. These substances can prevent the ink from properly adhering to the metal. Several cleaning methods can be employed, including using specialized cleaning solutions, degreasers, or isopropyl alcohol. Cleaning can be done by hand or with the aid of ultrasonic cleaners. The goal is to ensure the surface is spotless before proceeding to the next steps. The cleaning stage sets the foundation for a successful print and influences the overall quality of the final product.
Priming the Surface

Priming the surface is an essential step to improve ink adhesion and durability. Primers create a bonding layer between the metal surface and the ink, preventing peeling and enhancing the print’s longevity. Primers also help to create a smoother surface, which improves print quality and detail. The choice of primer will depend on the ink type and the metal alloy of the diecast model. Priming typically involves applying a thin, even layer of primer and allowing it to dry or cure according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Applying the primer correctly creates a more durable and appealing print.
Design and Artwork Considerations
Before printing, you need to prepare your design and artwork. This involves creating or modifying the graphics to fit the diecast model’s dimensions and printing method. The design considerations include the complexity of the design, the number of colors, and the level of detail required. You also have to consider the specific limitations of your printing technique. Careful design and artwork preparation will ensure a successful print and prevent issues such as color inaccuracy or smudging. Creating print-ready artwork is an important step in the diecast printing process.
File Format and Resolution
Selecting the appropriate file format and resolution is essential for producing high-quality prints. Vector graphics, such as those created in programs like Adobe Illustrator or CorelDRAW, are often preferred, because they can be scaled without any loss of quality. Raster images, such as JPEGs or PNGs, should have a high resolution to ensure sharp details. A high resolution, measured in dots per inch (DPI), is crucial to prevent pixelation or blurring of the design. When preparing your artwork, ensure that the file format and resolution are compatible with your printing equipment and the chosen printing technique. The correct file format and resolution result in a clear, sharp, and accurate reproduction of your design on the diecast model.
Color Profiles and Calibration

Accurate color reproduction is crucial for any diecast printing project. The use of color profiles and proper calibration ensures that the colors you see on your screen match the colors on the printed model. Color profiles, such as those based on the CMYK color model, help to manage and standardize color representation. Color calibration involves adjusting your monitor and printer to ensure that colors are displayed and printed accurately. This involves the use of color management software and colorimeters. Proper color management avoids color inconsistencies and ensures that your final product accurately reflects your design. Careful attention to color profiles and calibration ensures color accuracy.
Step-by-Step Diecast Printing Guide
The diecast printing process can be broken down into several key steps, from preparing the model to applying the design. Following these steps in the correct order is crucial for achieving consistent, high-quality results. Each step is as important as the last. Whether you’re using pad printing, screen printing, or digital printing, following a structured approach ensures that you avoid common mistakes and optimize the printing process. The goal is to provide a clear understanding of how to print on diecast models effectively. By systematically working through each step, you can ensure a successful diecast printing project.
Printing Process
The printing process begins after the diecast model has been prepared and the artwork is ready. The specific steps vary depending on the chosen printing technique. For pad printing, the printing plate is prepared, the ink is applied, and the image is transferred to the model using a silicone pad. Screen printing involves creating a stencil on a mesh screen and forcing the ink through the open areas. Digital printing involves directly printing the design onto the model using inkjet technology. The process of applying the ink must be performed carefully to ensure accurate registration of colors and a clean print. The printer settings are crucial for obtaining the desired results. The proper execution of the printing process leads to high-quality prints.
Curing and Finishing

After the ink has been applied, it must be cured or dried. The curing process ensures that the ink bonds permanently to the model. Curing methods vary depending on the ink type. Some inks dry through air exposure, while others require heat or UV light. Following the curing process, the model may undergo finishing touches. These steps might include applying a clear coat to protect the print and enhance its appearance. The clear coat adds a layer of protection against scratches and environmental factors, and also provides a professional look. Proper curing and finishing are vital for achieving a durable and visually appealing final product.
Common Problems and Solutions
Even with careful planning, problems can occur during diecast printing. These problems can range from ink smudging to poor adhesion and color inaccuracies. Understanding these common issues and knowing how to resolve them is essential for achieving high-quality results. Troubleshooting is an ongoing process, and learning to identify and correct these issues will save time and resources. By knowing how to identify and resolve these problems, you can significantly improve your diecast printing results.
Ink Smudging
Ink smudging is a common problem that occurs when the ink smears or blurs during the printing or curing process. This can result from several factors, including using the wrong type of ink, excessive ink on the printing plate, or improper curing. To prevent ink smudging, use the correct ink for your printing method, and ensure that the ink viscosity is properly adjusted. Ensure the curing process is followed carefully. If smudging occurs, cleaning the printing plate and adjusting the ink’s properties can help. Proper technique and the right equipment are vital in avoiding this issue.
Poor Adhesion
Poor adhesion occurs when the ink does not properly bond to the metal surface, resulting in prints that can easily scratch or peel off. This is typically caused by insufficient surface preparation, using the wrong ink, or incorrect curing. To improve adhesion, start with the surface preparation process, including thorough cleaning and priming. Ensure that the ink is compatible with the metal and follow the manufacturer’s recommended curing procedures. Inspect the model for any signs of adhesion problems, and make necessary adjustments to the printing process or materials. Proper adhesion is essential for the longevity of your print.
Color Inaccuracy
Color inaccuracies occur when the colors on the printed model do not match the original design or desired colors. This problem can be caused by incorrect color profiles, improper calibration of the printer and monitor, or variations in the ink. To avoid color inaccuracies, use color management software and properly calibrate your equipment. Ensure that the color profiles are correctly set up for your printing process. Regularly checking and adjusting the color settings can help ensure that the colors in your final prints match the original design. Paying attention to color accuracy enhances the visual quality of your models.
Maintaining Your Diecast Printing Equipment
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your diecast printing equipment in good working condition. Proper maintenance helps to prevent breakdowns, maintain print quality, and extend the life of your equipment. A well-maintained machine will also deliver more consistent results. Establishing a regular maintenance routine will save you time and expense in the long run. Keeping your equipment in good condition is an investment in your diecast printing projects.
Cleaning and Maintenance Routine
Develop and stick to a regular cleaning and maintenance schedule. This includes cleaning the printing heads, the printing plate, and other components, and checking for any wear and tear. Replace any worn parts promptly. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific cleaning procedures and maintenance recommendations. Regular inspections and maintenance will help to identify and fix potential issues before they become major problems. A well-maintained machine will perform optimally and provide consistently good results.
Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling of your diecast printing equipment and supplies are crucial for preserving their condition and extending their lifespan. Always store inks, solvents, and cleaning solutions in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Handle the printing equipment with care to prevent damage, and avoid dropping or mishandling parts. If you’re not using your equipment for an extended period, follow the manufacturer’s storage recommendations to protect your investment. Careful handling and storage contribute to the longevity of your equipment.
Where to Find More Information
For further information on diecast printing, several resources are available. Online resources, such as forums and blogs dedicated to model-making and printing, offer valuable tips, techniques, and troubleshooting advice. Manufacturers’ websites and product manuals provide detailed information on specific equipment and materials. Joining local hobby groups or attending workshops can also be a great way to learn from experienced modelers and experts. By exploring these resources, you can deepen your knowledge and enhance your skills in diecast printing.
